Medical engineering technology represents a vital intersection between engineering and medical sciences, aiming to enhance beauty and healthcare through innovative solutions. This field encompasses a wide array of applications, from developing advanced medical devices to pioneering novel treatment methods. Here we discuss the contributions of medical engineering technology in various specialized medical procedures, including treating cancer with stem cells, the lymphatic system, vaser liposuction, skin care, hair transplants, rhinoplasty, and hairline lowering surgery.
Beauty Treatments
Botox (1980s): Botulinum toxin (Botox) was first used for medical purposes to treat muscle spasms but later became popular in cosmetic treatments for reducing wrinkles and fine lines (Cad Crowd).
Laser Hair Removal (1960s): Developed as a method to permanently reduce unwanted hair, laser hair removal uses concentrated light beams to target and destroy hair follicles (Cad Crowd).
Chemical Peels (1950s): Chemical peels use acids to remove the outer layers of skin, treating wrinkles, scars, and discoloration to improve skin appearance (Cad Crowd).
Cosmetic Surgery
Rhinoplasty (1920s): Modern rhinoplasty techniques were developed in the early 20th century, allowing for the reshaping of the nose for both cosmetic and functional purposes (Cad Crowd).
Breast Implants (1962): Thomas Cronin and Frank Gerow developed silicone breast implants, which have become a common procedure for breast augmentation and reconstruction (Cad Crowd).
Liposuction (1974): Invented by Italian and French surgeons, liposuction is a technique for removing excess fat from specific areas of the body, improving body contours and proportions (Cad Crowd).
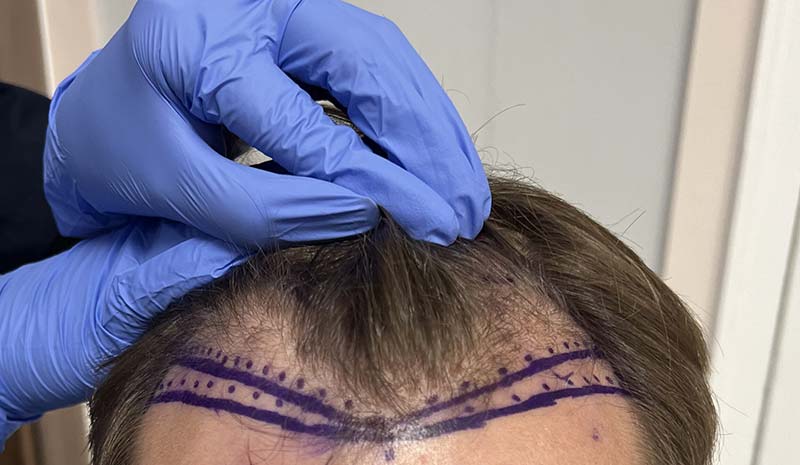
Hair Transplants
Hair Transplant Surgery (1950s): Dr. Norman Orentreich pioneered hair transplantation techniques, which involve moving hair follicles from one part of the body to bald or thinning areas to restore hair growth (Cad Crowd).
Follicular Unit Transplantation (1990s): This technique involves transplanting hair in its naturally occurring groups of 1-4 hairs, resulting in a more natural appearance and better outcomes for patients (Cad Crowd).
Skin Care
Retinoids (1970s): Originally developed to treat acne, retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) have become popular for their anti-aging properties, improving skin texture and reducing wrinkles (Cad Crowd).
Sunscreen (1938): Developed by chemist Franz Greiter, modern sunscreens protect the skin from harmful UV rays, preventing sunburn and reducing the risk of skin cancer (Cad Crowd).
Moisturizers (20th Century):
Advancements in dermatology led to the development of various moisturizers that help maintain skin hydration, prevent dryness, and improve skin barrier function (Cad Crowd).
These innovations have significantly advanced medical treatments and cosmetic procedures, enhancing both health outcomes and aesthetic possibilities for individuals.
Stem cells for cancer treatment, invented in the 20th century.
Treating cancer with stem cells, a groundbreaking 20th-century invention, leverages the unique ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types. This innovative approach involves engineering stem cells to target and deliver therapies directly to tumor sites, potentially regenerating damaged tissues and effectively combating cancer. This advancement represents a significant leap in oncology, offering new hope for more precise and effective cancer treatments.
The lymphatic system
The 20th century saw significant advancements in the study and treatment of the lymphatic system, including the development of lymphangiography for imaging lymphatic vessels, nuclear medicine techniques like lymphoscintigraphy for non-invasive diagnostics, and improved understanding and management of lymphatic diseases such as lymphomas and lymphedema.