Who invented Hair Transplants for Thinning Hair
Hair transplants - a history and overview
Hair transplantation has evolved into one of the most sophisticated and sought-after cosmetic procedures in the world, but its roots stretch back nearly a century. The history of hair and its profound cultural significance underscore why the desire to restore it remains so powerful. Modern techniques like FUE hair transplantation offer patients natural results with minimal downtime, but this progress is built on decades of pioneering work. In the 1930s, Japanese dermatologist Shoji Okuda laid the groundwork by experimenting with grafting skin and hair, although his research remained largely unknown outside Japan due to World War II.
It wasn’t until the 1950s that Norman Orentreich, a New York dermatologist, who invented hair transplants, brought hair transplantation into the global spotlight. His discovery—that hair taken from the back of the scalp retained its resistance to balding when moved to thinning areas—was revolutionary. This principle of “donor dominance” became the cornerstone of modern hair restoration. The history of hair transplantation since then has been marked by constant refinement, leading to the minimally invasive FUE hair method. In FUE, individual follicles are extracted and re-implanted with precision, allowing for natural hairlines and dense coverage without a visible scar. The procedure appeals to both men and women, offering hope to those who have struggled with hair loss for years.
As the history of hair continues to unfold, it is clear that hair transplantation—especially FUE hair techniques—has become more than just a medical solution; it’s a deeply personal journey of identity, confidence, and renewal.
Hair loss is a common issue affecting people worldwide,
with causes ranging from genetics to lifestyle factors. Fortunately, improvements in technology have led to highly effective hair transplant procedures that help restore hair and confidence. This article explores the causes of hair loss, hair restoration options, the hair transplant procedure, and what to expect from transplanted hair.
Wikipedia covers its history here
Understanding Hair Loss
Hair loss, often referred to as alopeica, is due to various reasons, including genetics, hormon changes, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions. The most common form of hair loss is male and female pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), which results from hereditary factors and hormonal fluctuations.
Other causes include:
- • Telogen Effluvium: Temporary hair shedding due to stress, illness, or medication.
• Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition causing patchy hair loss.
• Traction Alopecia: Hair loss due to excessive pulling or tight hairstyles.
- • Telogen Effluvium: Temporary hair shedding due to stress, illness, or medication.
Regardless of the cause, hair loss can significantly impact self-esteem and overall well-being, prompting many individuals to seek hair restoration solutions.
Hair Restoration: What Are the Options?
Hair restoration encompasses various treatments aimed at preventing further hair loss and regrowing hair. Some of the most common options include:
1. Medications: FDA-approved treatments such as minoxidil and finasteride can slow hair loss and promote regrowth in some individuals.
2. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Laser caps and combs stimulate hair follicles, enhancing growth and reducing shedding.
3. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): A non-surgical solution that creates the appearance of a fuller head of hair by tattooing pigment into the scalp.
4. Hair Transplant Surgery: The most effective long-term solution for hair loss, which involves redistributing healthy hair follicles to balding areas.
Among these options, hair transplant surgery stands out as the only permanent and natural-looking hair restoration method.
The Hair Transplant Procedure Explained
A hair transplant is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that redistributes healthy hair follicles from a donor area to thinning or balding areas. There are two primary techniques:
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Also known as the strip method, is where a thin strip of scalp is remived from the donor area. The strip is then cut into separate follicular units, which are implanted into the recipient site. FUT allows the transplantation of a large number of folicle grafts in one session, it leaves a linear scar on the donor site.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more up-to-date technique where individual follicles are extracted from the donor area using a micropunch and implanted into the balding regions. This method leaves far less scarring and is a faster recovery time compared to FUT.
3. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
A variation of FUE, DHI uses a specialized implanter pen to insert hair follicles directly into the scalp, ensuring precise placement and natural-looking results.
Each method has its pros and cons, and the choice depends the extent of hair loss, scalp condition, and patient preference.
What to Expect from Transplanted Hair
After a hair transplant, the newly implanted follicles go through several stages:
• Initial Shedding (First Few Weeks): Transplanted hairs fall out due to the shock of relocation. This is a normal part of the process.
• Dormant Phase (Up to 3 Months): The follicles remain inactive before starting new growth.
• Growth Phase (3+ Months): New hairs begin to emerge, gradually thickening and blending with natural hair.
• Final Results (12+Months): Full density and natural appearance are achieved, with permanent hair growth.
Transplanted hair is like natural hair and can be washed, cut, and styled normally. It is resistant to the hormones that cause hair loss, making it a lifelong solution.
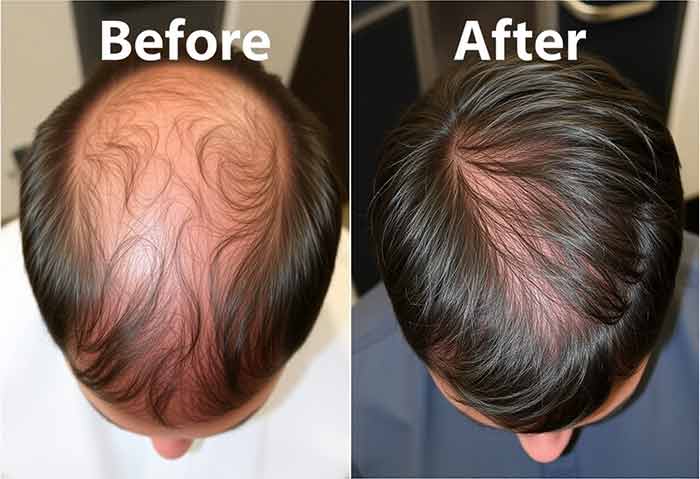
Who is Suitable for a Hair Transplant?
Not everyone experiencing hair loss is an ideal candidate for a hair transplant. Suitable candidates generally:
• Have plenty of donor hair at the back or sides of the scalp.
• Experience pattern baldness rather than diffuse thinning.
• Are in good health and have realistic expectations about the results.
• Have slow hair loss.
Cost and Market Trends
Hair transplant costs vary significantly based on location, technique, and clinic reputation. In the UK, the average cost ranges from £1,995 to £15,000, depending on the extent of the procedure. One of the better-known clinics for a London hair transplant is The Mittal Hair Clinic.
Factors influencing price include:
• The number of grafts required.
• The surgeon’s expertise.
• The clinic’s facilities and reputation.
• The chosen transplant method (FUE tends to be more expensive than FUT).
Many UK residents travel abroad, particularly to Turkey, where hair transplant costs are lower due to reduced overhead expenses. However, while affordability is attractive, it is important to pick a reputable clinic with qualified professionals to avoid complications.
Risks and Considerations
While hair transplants are generally safe, risks include:
• Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar, while FUE may cause tiny scars.
• Infection: Rare but possible if instructions are not followed.
• Shock Loss: Temporary loss of surrounding hair.
• Unnatural Results: Poorly planned transplants may result in an unnatural hairline or density.
To minimize risks, it is critical to choose a board-certified and experienced surgeon specializing in hair restoration.
Post-Procedure Care
Proper aftercare is important for successful healing and optimal hair growth. Key guidelines include:
• Avoid touching or scratching the scalp for the first few days.
• Sleep with your head on 2 pillows to reduce swelling.
• Follow prescribed medications to prevent infection and inflammation.
• Don’t carry out physical activity for at least two weeks.
• Use gentle shampoos and follow the clinic’s washing instructions.
Hair transplants have changed the field of hair restoration, offering individuals a permanent, natural-looking solution to hair loss. Today, patients can have minimally invasive procedures with very good results. However, choosing a reputable surgeon, and following their proper aftercare are essential steps for the best outcome.
For those struggling with thin hair, a hair transplant can restore not only hair but also self-confidence and a life-changing decision worth considering.
Hair transplant vs. non surgical treatments | |||||
Treatment | Mechanism | Best For | Effectiveness | Longevity | Clinical Backing |
Hair Transplant (FUE/FUT) | Graft transplantation of DHT-resistant follicles | Advanced hair loss | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (85–95% survival) | Permanent | Yes – Long-term studies confirm effectiveness |
Minoxidil | Topical vasodilator, prolongs anagen phase | Early thinning | ⭐⭐☆☆☆ (60–70% efficacy) | Temporary (needs daily use) | FDA-approved & peer-reviewed trials |
Finasteride | Oral 5α-reductase inhibitor (reduces DHT) | Early-to-moderate (men) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (80–90% response) | Temporary | FDA-approved & multi-year RCTs |
PRP Therapy | Platelet-derived growth factors stimulate follicles | Adjunctive, early thinning | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (70–80% benefit) | Semi-permanent | Growing body of meta-analyses & trials |
Comparative Effectiveness (Based on Clinical Data) | |||
Treatment | % of Users with Improvement | Duration of Results | Ideal For |
Hair Transplant | 90–95% (long-term growth) | Permanent | Moderate to advanced loss |
Minoxidil | 60–70% | Temporary | Early thinning |
Finasteride | 80–90% | Temporary | Early-to-moderate loss (men only) |
How do hair transplants work?
Hair transplants relocate follicles from donor areas (typically the back of the head) to thinning or balding regions. The transplanted follicles continue to grow hair naturally in their new location.
Are hair transplant results permanent?
Yes, transplanted hair is typically permanent as it comes from areas resistant to baldness. However, existing hair may continue to thin, potentially requiring additional procedures later.
How long until I see results after a transplant?
Transplanted hair typically falls out within 2-3 weeks post-procedure, then begins regrowth after 3-4 months. Full results usually become visible between 9-12 months.
Is a hair transplant procedure painful?
Most patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure thanks to local anesthesia. Some soreness, swelling, and tenderness may occur during the recovery period.
Who is an ideal candidate for hair transplantation?
Ideal candidates are those with stable hair loss, sufficient donor hair, realistic expectations, good general health, and typically over 25 years old to establish hair loss patterns.
What's the difference between FUT and FUE transplants?
FUT (strip method) removes a strip of scalp, while FUE extracts individual follicles. FUE leaves tiny scars rather than a linear one and typically has a shorter recovery time.
- American Academy of Dermatology Association: https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-loss
- International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery: https://ishrs.org/
Author: Dr. Manish Mittal, founder of The Mittal Hair Clinic
